- Home
- Common Foot Problems
- Os Trigonum
Os Trigonum Syndrome
Written By: Chloe Wilson BSc(Hons) Physiotherapy
Reviewed By: FPE Medical Review Board
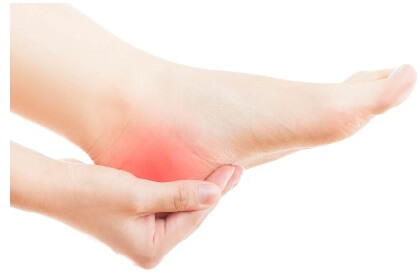
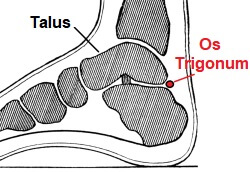
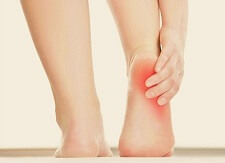
Os Trigonum causes posterior ankle pain due to a small, extra bone found at the back of the ankle.
Also known as posterior talar impingement or posterior ankle impingement, Os Trigonum Syndrome typically causes pain and stiffness at the ankle which tends to be worse when pointing your toes.
There is often swelling and you may be able to feel a small lump behind the ankle which is often tender to touch.
This extra bone formation is fairly rare and only occurs in approximately 5-10% of people. Often it goes completely unnoticed, not causing any problems.
However, when combined with an ankle injury or in athletes who sports require frequent ankle flexion e.g. ballet dancers and footballers, Os Trigonum Syndrome can develop.
What Is An Os Trigonum?
An Os Trigonum is a small, accessory bone that forms at the back of the foot behind the ankle joint.
Quick anatomy lesson. The talus bone forms part of the ankle joint. As the talus grows during childhood, a small piece of bone develops just behind it, known as the Os Trigonum. This usually happens around the ages of seven to eleven.
This small bone is initially joined to the talus by fibrous structures and within one to three years, usually fuses i.e. joins with the talus bone forming part of the lateral tubercle, a small lump on the talus.
However, sometimes it fails to join the talus and remains a separate piece of bone. It is usually small, less than one centimetre, and varies in shape from round to oval to triangular.
Usually, if the bone fails to fuse it doesn’t cause any problems, but if the ankle is injured, either through a specific incident or recurrent trauma, Os Trigonum Syndrome can develop which causes pain and stiffness at the back of the ankle.
What Causes Os Trigonum Syndrome?
Os trigonum syndrome typically develops when there is a foot or ankle injury, usually from:

- Over-Use: from repeated plantarflexion (foot pointing downwards). Os Trigonum Syndrome commonly affects ballet dancers, runners and football players
- Trauma: an ankle injury where the foot is forced into excessive plantarflexion
Either of these can cause what is known as a “nutcracker injury”, where the unfused Os Trigonum bone and surrounding soft tissues become wedged between the ankle and heel bones (tibia, talus and calcaneus). The soft tissues become inflamed leading to pain and stiffness. It is the irritation of the soft tissues that causes Os Trigonum Syndrome.
There is no specific age or gender that is more susceptible to Os Trigonum Syndrome, it is purely related to activity.
Symptoms Of Os Trigonum
The most common symptoms of Os Trigonum syndrome are:
- Foot Pain: Usually at the back of the ankle. The pain tends to be worse when plantarflexing the foot (pointing the toes) or during the push-off phase of walking and eases with rest
- Tenderness: It is usually tender to touch the area at the back and outer side of the ankle
- Swelling: swelling may develop due to the inflammation of the soft tissues
- Lump: sometimes you may be able to feel a small, hard lump near the Achilles tendon. This is the unfused bone
The condition usually affects one foot, but in approximately one third of cases, both feet are affected.
How Is It Diagnosed?
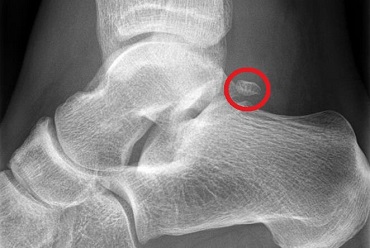
Your doctor will suspect this os trigonum syndrome from your signs and symptoms and by ruling out other conditions.
They may want to confirm the diagnosis with an x-ray or MRI scan as the symptoms are often similar to other conditions such as achilles tendonitis and tarsal tunnel syndrome.
It is really important to get an accurate diagnosis to ensure you get the correct treatment. The earlier you start treatment, the quicker os trigonum syndrome will resolve.
Os Trigonum Treatment
The main aim of os trigonum treatment is to allow the soft tissues to heal so the inflammation can settle, which is done through a combination of:
1. RICE
Rest, ice, compression and elevation are the best place to start with treatment for os trigonum.
Complete rest for four to six weeks from all activities that irritate the condition is highly recommended to allow time for the inflammation to settle. You may be given a walking boot to wear to restrict ankle movement when you are up and about
Regularly applying ice to the back of the ankle also helps reduce swelling and inflammation. Visit the ice section to find out how to safely and effectively use ice therapy
2. Medication
Your doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory medications such as NSAIDs like ibuprofen to help reduce swelling and pain from os trigonum syndrome. Always talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking any new medication.
3. Steroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections are sometime used to reduce pain and inflammation. You can find out more about how they work and the common side effects in the injections section on out sister site
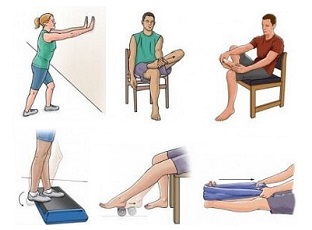
4. Exercises
Working on a rehab programme of stretching and strengthening exercises with a physiotherapist can also really help.
Strengthening the ankle and foot muscles can help the talus to glide forwards slightly during plantarflexion which can help reduce the pressure on the Os Trigonum and thus preventing the irritation of the soft tissues.
5. Surgery
If symptoms persist, surgery may be advised to remove the small piece of bone. This should be followed with a course of physiotherapy. The outcome is usually extremely good with full resolution of symptoms and you can usually return to sports after four to eight weeks.
Differential Diagnosis
Os Trigonum is quite a rare cause of foot pain and there are a number of other conditions that present with similar symptoms:
- Foot Tendonitis: inflammation of one of the foot tendons
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome: compression of one of the foot nerves
- Achilles Tendonitis: inflammation or degeneration of the achilles tendon
- Heel Bursitis: Inflammation of the fluid filled sac behind the ankle
- Heel Spurs: Extra growths of bone on the heel
With any case of foot pain it is really important to seek medical advice to ensure you get an accurate diagnosis.
Recovery Process
It usually takes about 4-6 weeks from an acute bout of os trigonum syndrome, if treatment is started swiftly.
However, if symptoms have been present for a few months, or if you are someone who is very active, particularly sports players, then it can take much longer for things to settle down.
It is important to rest from all aggravating activities and once symptoms have fully resolved, to take it very slowly getting back to your previous activities otherwise your symptoms are likely to return. Working with a physical therapist on a rehab program is vital.
Os Trigonum Summary
Os Trigonum is a common cause of posterior ankle pain and stiffness at the back of the foot.
It is caused by a small, bone at the back of the ankle that fails to fuse during adolescence that gets irritated from an ankle injury or repetitive plantarflexion.
Common symptoms of os trigonum include pain behind the ankle, tenderness, swelling and a small hard lump behind the heel.
Treatment for os trigonum syndrome usually involves a combination or rest, ice, medication, exercises, steroid injections and occasionally surgery.
If Os Trigonum doesn't sounds quite like your problem, visit the heel pain section for other common causes of pain behind the ankle, or visit the foot pain diagnosis section for help working out what is wrong.
You may also be interested in the following articles:
- Pain On Top Of Foot
- Foot Arch Pain
- Nerve Pain In The Foot
- Foot & Ankle Stretches
- Swollen Feet & Ankles
- Foot Numbness
Related Articles
Page Last Updated: 02/28/24
Next Review Due: 02/22/26