- Home
- Common Foot Problems
- Avulsion Fractures
Pseudo Jones Fracture
Written By: Chloe Wilson BSc(Hons) Physiotherapy
Reviewed By: FPE Medical Review Board
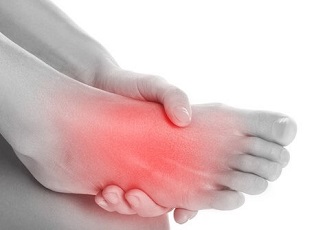
A Pseudo Jones fracture, aka avulsion fracture, is a common foot injury.
These fractures occur at the base of the fifth metatarsal, the long bone on the outer side of the foot.
Pseudo Jones fractures typically result from sudden twists, rolls or impacts to the ankle or foot. They cause outer foot pain and swelling and often interfere with daily activities such as walking.
Despite being the most common type of fifth metatarsal fracture, they usually heal well with simple treatment. Occasionally, surgery may be required.
Here we will look at what a Pseudo Jones fracture is, the common causes and symptoms, how avulsion fractures are diagnosed, the best treatment options and the recovery process.
What Is a Pseudo Jones Fracture?
A Pseudo Jones fracture is an avulsion fracture that occurs when a small piece of bone is pulled away from the base of the fifth metatarsal.
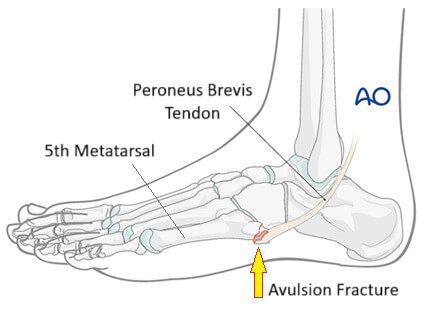
The fifth metatarsal is the long bone on the outer side of the foot that connects the mid-foot to the pinky toe.
At the base of the fifth metatarsal is an area known as the tuberosity, a bony prominence on the outside of the foot. The peroneus brevis tendon attaches directly to the tuberosity.
If the foot or ankle is suddenly forced inwards, it pulls on the peroneus brevis tendon. If the force is strong enough, the tendon is torn away from the tuberosity, pulling a small fragment of bone with it. This is known as an avulsion fracture foot or Pseudo Jones fracture.
The injury is often confused with a true Jones fracture, which occurs slightly further along the bone and has more serious implications due to limited blood flow in that area. However, avulsion fractures typically heal faster because the affected area has a good blood supply.
Pseudo Jones fractures may also be incorrectly referred to as a Dancer’s Fracture, but these also occur further down the fifth metatarsal and are treated slightly differently.
Causes Of Pseudo Jones Fracture
Fifth metatarsal avulsion fractures are commonly caused by:
- Inversion Injuries: Rolling the ankle inwards is the most common cause of a Pseudo Jones fracture as it places excessive stress on the lateral ligaments and tendons. This sudden twisting movement is common during sports, on uneven ground, or when tripping over something e.g. a kerb or step
- Direct Trauma: A sharp blow to the outer edge of the foot, such as dropping something heavy or being kicked, can cause the bone to fracture
- Repetitive Stress: Overuse injuries from activities like running, jumping, or dancing can strain and weaken the area over time, making it more susceptible to fractures.
Fifth metatarsal avulsion fractures are especially common in athletes and individuals engaging in high-impact activities.
Avulsion fractures are the most common type of fracture of the fifth metatarsal. Approximately 68% of all metatarsal fractures occur in the fifth metatarsal of which 90% are Pseudo Jones fractures.
Symptoms of Avulsion Fracture Foot
Common symptoms of a Pseudo Jones fracture are:
- Localized Pain: Sharp, stabbing outer foot pain at the base of the fifth metatarsal, especially when bearing weight
- Swelling and Bruising: Swelling on the outer side of the foot, often accompanied by bruising that may extend to the ankle and toes
- Tenderness: The base of the fifth metatarsal is usually painful to touch
- Difficulty Walking: Limited ability to walk or put weight on the affected foot, often causing you to limp
- Deformity: In severe cases, there may be a visible or palpable lump on the side of the foot, although this is quite rare
Diagnosing Avulsion Fractures
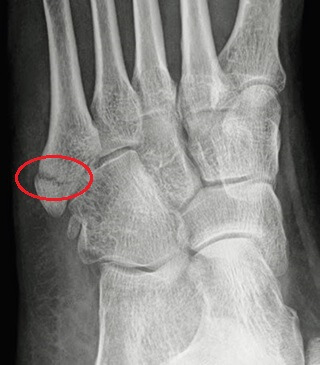
A Pseudo Jones fracture can often be mistaken for other types of foot injury, such as a true Jones fracture or a severe ankle sprain, so accurate diagnosis is essential.
- History: Your doctor will start by asking you about your foot symptoms including when and how they started, what makes the pain better or worse, how the pain is impacting your daily activities, any previous foot injuries and other medical conditions.
- Physical Examination: They will then examine your foot, assessing for pain, swelling and tenderness at the base of the fifth metatarsal. They will also evaluate the range of motion and strength in the foot and ankle.
- Imaging Tests: If your doctor suspects an avulsion fracture foot, they will send you for imaging studies. Standard X-rays are typically sufficient to identify a Pseudo Jones fracture, its location, the severity and any other associated bony injuries. An MRI or CT Scan is rarely needed but may be used to detect subtle fractures or associated soft tissue injuries.
Differential Diagnosis
Differentiating a Pseudo Jones fracture from other foot injuries is critical, as they will have different treatments and healing outcomes. There are a number of other injuries that can present in a similar way to an avulsion fracture foot:
- Jones Fracture: a break slightly further down the fifth metatarsal, in a zone with poor blood supply, which has a higher risk of healing complications. FIND OUT MORE >
- Ankle Sprain: Overstretching or tearing of one of the ankle ligaments resulting in pain and instability. FIND OUT MORE >
- Cuboid Syndrome: Where the cuboid bone which sits next to the fifth metatarsal shifts out of place, usually following an inversion injury. FIND OUT MORE >
- Dancer’s Fracture: an oblique or spiral fracture that occurs in the shaft of the fifth metatarsal. FIND OUT MORE >
- Peroneal Tendonitis: inflammation of peroneal tendon due to overuse or sudden increases in training. FIND OUT MORE >
- Stress Fractures: a small break further down the fifth metatarsal from repetitive over-loading. FIND OUT MORE >
Treatment Of Pseudo Jones Fracture
Pseudo Jones fractures generally heal well with non-surgical treatment due to the area’s good blood supply.
Treatment of a Pseudo Jones fracture typically involves:
- Immobilization: A walking boot or short leg cast is used to stabilize the foot and allow the bone to heal in the correct position. This is typically worn for 4–6 weeks
- Rest and Weight Bearing: Initially, non-weight-bearing with crutches may be recommended for 4-6 weeks. As healing progresses, weight-bearing can be gradually reintroduced
- Ice: Regularly applying ice packs to the area helps to reduce pain and swelling which can speed up the healing process. Ideally you want to ice the outer foot for 10-15 minutes every 2-3 hours when possible in the first few weeks
- Elevation: When sitting, keep your foot and leg elevated, ideally higher than heart level. This helps reduce swelling as it encourages excess fluid to drain away from the foot. Leg elevation cushions can be particularly useful at night to keep your foot elevated while you sleep
- Medication: Over-the-counter medications such as paracetamol/acetaminophen or ibuprofen/Advil can help alleviate discomfort and swelling
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy is often recommended to restore strength, mobility, and balance in the foot after immobilization. Strengthening exercises, ankle mobility exercises and stability exercises are important to ensure you return to full function and to reduce the risk of further ankle injuries
- Surgical Treatment: Surgery is rarely needed for a Pseudo Jones fracture unless the bone fragment is significantly displaced or the fracture fails to heal with conservative care. Surgery typically involves using screws or wires to stabilize the bone fragment
Recovery Timeline
Most people recover well from a Pseudo Jones fracture, getting back to normal activities of daily living within 6–8 weeks, but this may vary depending on the severity of the fracture and individual healing capacity.
Athletes or individuals returning to high-impact activities may require additional time to regain full functionality. It may take 3-4 months to get back to your pre-injury level.
Jones vs Pseudo Jones Fracture
There is often some debate as to the difference between a Pseudo Jones fracture and a true Jones fracture. It all comes down to the location of the injury.
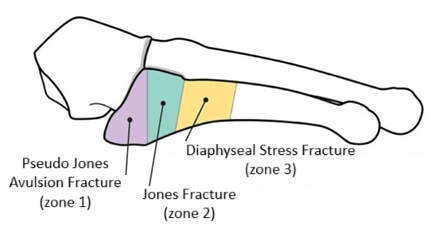
The base of the fifth metatarsal can be divided into different zones.
Pseudo Jones avulsion fractures occur in the zone 1 region, at the proximal end of the metatarsal base.
They may or may not extend to the articular surface – if they do they are known as an intra-articular fracture.
A true Jones fracture occurs in the zone 2 region, slightly further down the bone, an area known as the proximal diaphysis. Jones fractures never extend to the articular surface, they are always extra-articular.
The main difference between the two zones is the blood supply. Zone 1 has a strong blood supply which allows for efficient and effective healing. Zone 2 however is an area with very limited blood supply, known as a watershed area, so healing from a Jones fracture is often delayed and there is a high incident of non-union. This is why Jones fractures are much more likely to require surgical intervention than a Pseudo Jones fracture.
Pseudo Jones Fracture Summary
A Pseudo Jones fracture, or avulsion fracture of the fifth metatarsal, is a relatively minor but painful injury that typically results from rolling the ankle or direct trauma. It is less severe than a true Jones fracture and has a better healing prognosis due to its location in a well-vascularized area.
With appropriate treatment, such as immobilization, rest, gradual weight-bearing and physical therapy, most people recover within a few weeks without long-term complications.
If you suspect a Pseudo Jones fracture, prompt diagnosis and treatment are key to ensuring a smooth recovery and preventing further injury.
You may also be interested in the following articles:
- Fifth Metatarsal Fractures
- Lateral Foot Pain
- Lump On Outside Of Foot
- How To Treat Foot Swelling
- Foot Bones
- How To Do Stairs With Crutches
Related Articles
References
- Fifth Metatarsal Fractures And Current Treatment. World Journal Of Orthopedics
- Avulsion Fracture Of The 5th Metatarsal Tuberosity. Radiopaedia
- Proximal Avulsion Fractures Of The 5th Metatarsal (Pseudo-Jones). AO Surgery Reference
Page Last Updated: 28th November, 2024
Next Review Due: 28th November, 2026